39 vector biology definition
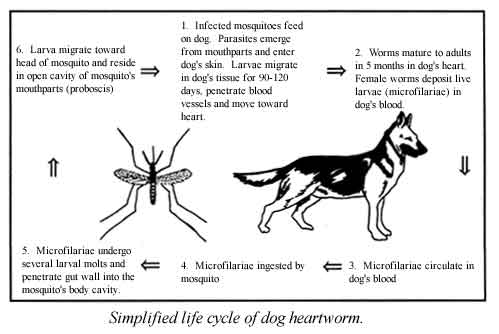
Medical Definition of Vector - MedicineNet Vector: In medicine, a carrier of disease or of medication. For example, in malaria a mosquito is the vector that carries and transfers the infectious agent. In molecular biology, a vector may be a virus or a plasmid that carries a piece of foreign DNA to a host cell. CONTINUE SCROLLING OR CLICK HERE QUESTION What causes tooth decay? See Answer Biological vector | definition of biological vector by Medical dictionary vector [ vek´tor] 1. a carrier, especially the animal (usually an arthropod) that transfers an infective agent from one host to another. Examples are the mosquito that carries the malaria parasite Plasmodium between humans, and the tsetse fly that carries trypanosomes from other animals to humans.
What is a Vector in Maths? (Definition, and Components) - BYJUS In maths, a vector is a quantity that not only describes the magnitude but also describes the movement of an object or the position of an object with respect to another point or object. It is also known as Euclidean vector, geometric vector or spatial vector.

Vector biology definition
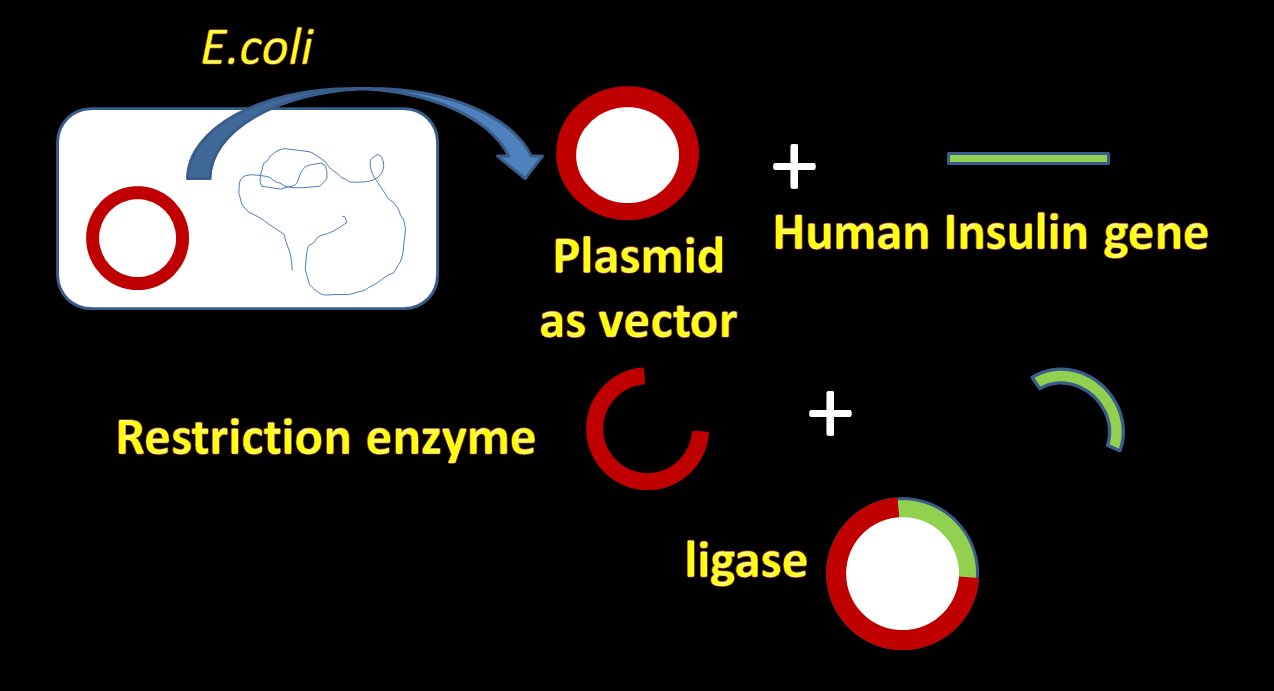
Vector (biology) - ScienceDaily Vector (biology) Traditionally in medicine, a vector is an organism that does not cause disease itself but which spreads infection by conveying pathogens from one host to another. Note: The above... Vector Definition in Science - ThoughtCo Vector Definition in Biology and Medicine In the biological sciences, the term vector refers to an organism that transmits a disease, parasite, or genetic information from one species to another. Examples: Mosquitoes are a vector of malaria. A virus may be used as a vector to insert genes into a bacterial cell. Cite this Article Vector - Genome.gov Definition 00:00 … A vector, as related to molecular biology, is a DNA molecule (often plasmid or virus) that is used as a vehicle to carry a particular DNA segment into a host cell as part of a cloning or recombinant DNA technique. The vector typically assists in replicating and/or expressing the inserted DNA sequence inside the host cell.
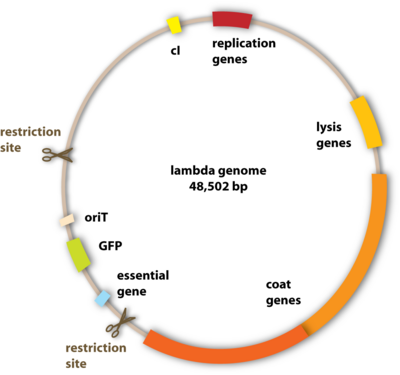
Vector biology definition. Medical Definition of Vector - RxList Definition of Vector vector Vector: In medicine, a carrier of disease or of medication. For example, in malaria a mosquito is the vector that carries and transfers the infectious agent. In molecular biology, a vector may be a virus or a plasmid that carries a piece of foreign DNA to a host cell. QUESTION From Healthy Resources Featured Centers Vector | definition of vector by Medical dictionary - TheFreeDictionary.com vec·tor. ( vek'tŏr) 1. An invertebrate animal (e.g., tick, mite, mosquito, bloodsucking fly) capable of transmitting an infectious agent among vertebrates. 2. Anything (e.g., velocity, mechanical force, electromotive force) having magnitude and direction; can be represented by a straight line of appropriate length and direction. 3. What Is a Vector? - Definition & Types - Study.com A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude (numerical size) and direction. This is the opposite of a scalar, which is a quantity that only has magnitude and no direction. So for example, a car... Vector (molecular biology) - Wikipedia Vector (molecular biology) In molecular cloning, a vector is any particle (e.g., plasmids, cosmids, Lambda phages) used as a vehicle to artificially carry a foreign nucleic sequence - usually DNA - into another cell, where it can be replicated and/or expressed. [1] A vector containing foreign DNA is termed recombinant DNA.
National Center for Biotechnology Information National Center for Biotechnology Information vector definition vector Definition: Search for: Glossary - word Glossary - def Textbooks Protocols Images Tools Forum PubMed Links Press Releases Vector (biology) Facts for Kids | KidzSearch.com A vector in biology is an animal on or in which a small living thing gets transported. The vector gets no benefit and sometimes loses fitness by the arrangement. The term is most used for the transport of parasites and agents of infection or disease. So, deadly diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever, are carried by some mosquitoes . What is a Vector in Math? - Definition & Examples - Study.com A vector represents a quantity that has both magnitude (distance) and direction. For example, when you travel 16 kilometers south, your journey may be represented as a vector quantity. We know ...
Vector - Entomologists' glossary - Amateur Entomologists' Society Vector. A vector is an organism that acts as an intermediary host for a parasite. Most importantly the vector transfers the parasite to the next host. Good examples of vectors are the mosquito in transmitting malaria and ticks in transferring Lyme disease. In the case of malaria, the mosquito becomes infected by feeding on the blood of an ... Vector Definition & Meaning | Britannica Dictionary Britannica Dictionary definition of VECTOR. [count] 1. mathematics : a quantity (such as velocity) that has size and direction. 2. technical : the course or direction of an airplane. 3. biology : an insect, animal, etc., that carries germs that cause disease. a mosquito that is the principal vector of yellow fever. Biologic vector - definition of biologic vector by The Free Dictionary n. A preparation that is synthesized from living organisms or their products, especially a human or animal protein, such as a hormone or antitoxin, that is used as a diagnostic, preventive, or therapeutic agent. Also called biological drug. adj. Variant of biological. Vector - Wikipedia Vector (molecular biology), a DNA molecule used as a vehicle to artificially carry foreign genetic material into another cell Cloning vector, a small piece of DNA into which a foreign DNA fragment can be inserted for cloning purposes Shuttle vector, a plasmid constructed so that it can propagate in two different host species
Vector Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster Definition of vector (Entry 1 of 2) 1 a : a quantity that has magnitude and direction and that is commonly represented by a directed line segment whose length represents the magnitude and whose orientation in space represents the direction broadly : an element of a vector space b : a course or compass direction especially of an airplane
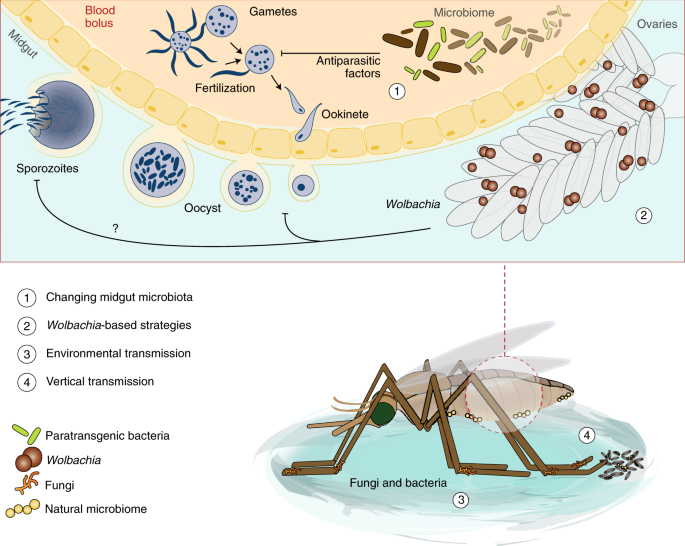
Vector-borne diseases | EFSA - European Food Safety Authority A vector is a living organism that transmits an infectious agent from an infected animal to a human or another animal. Vectors are frequently arthropods, such as mosquitoes, ticks, flies, fleas and lice. Vectors can transmit infectious diseases either actively or passively:
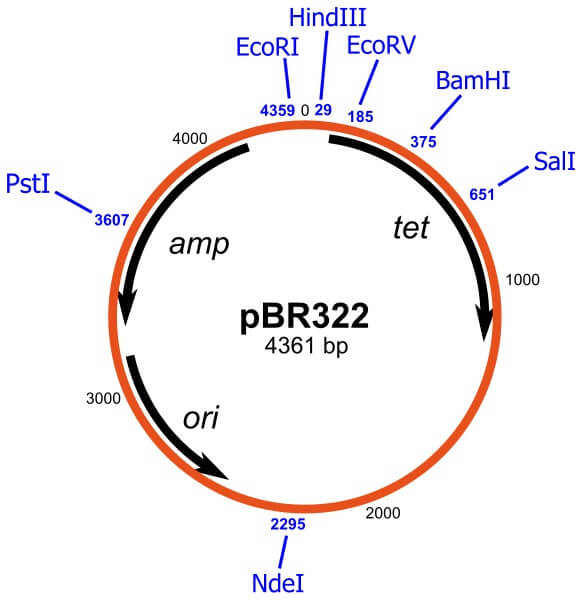
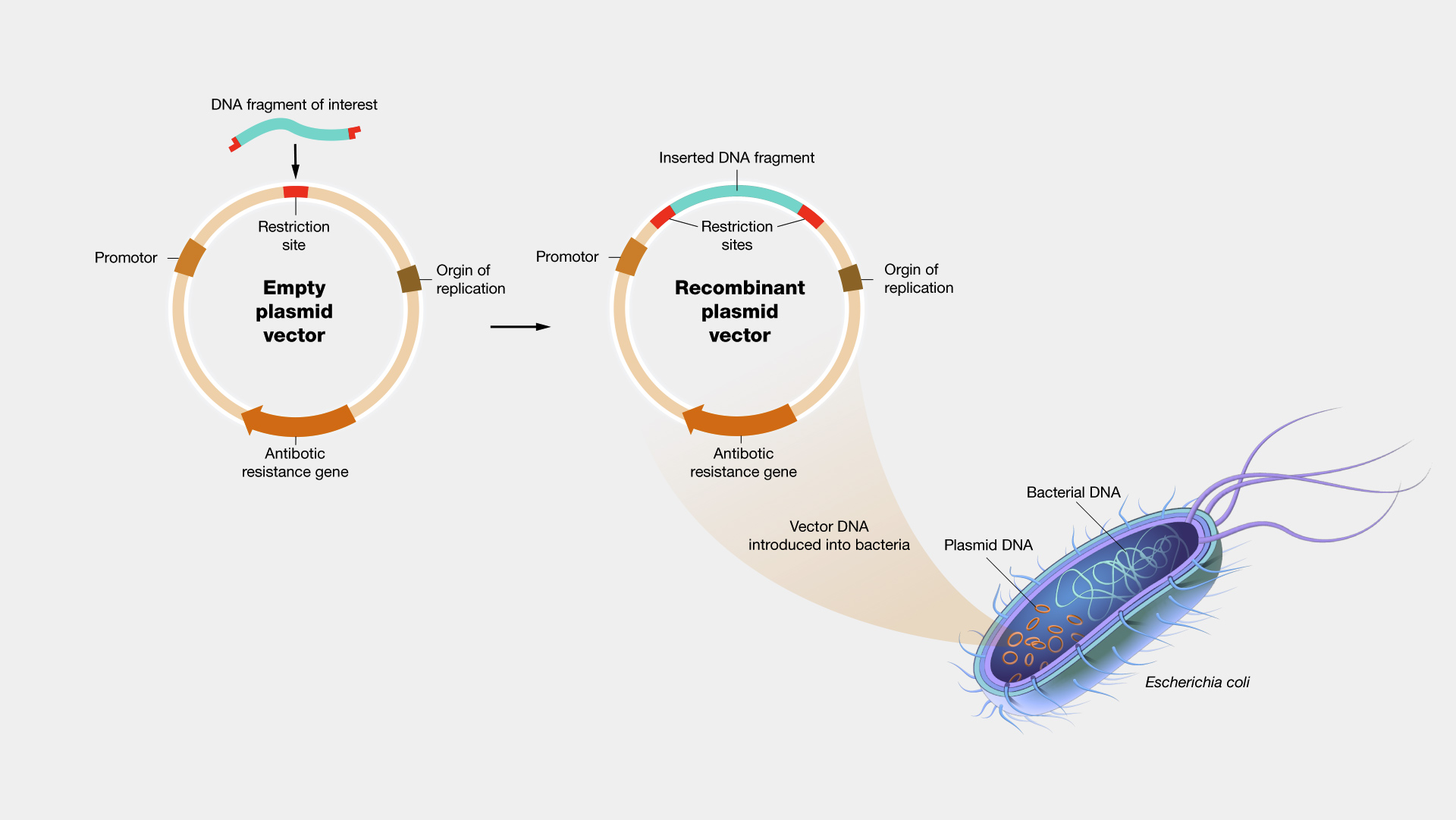
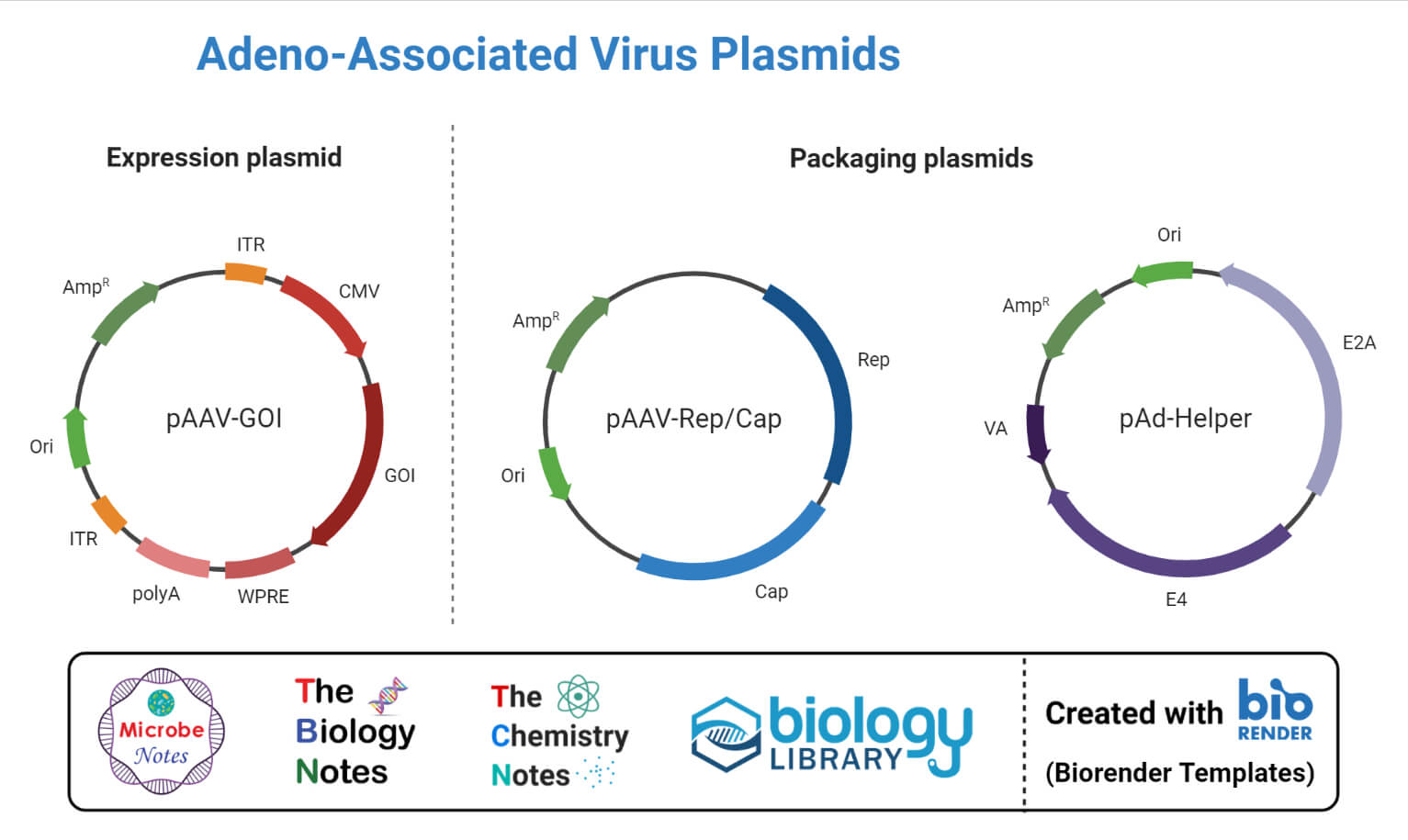
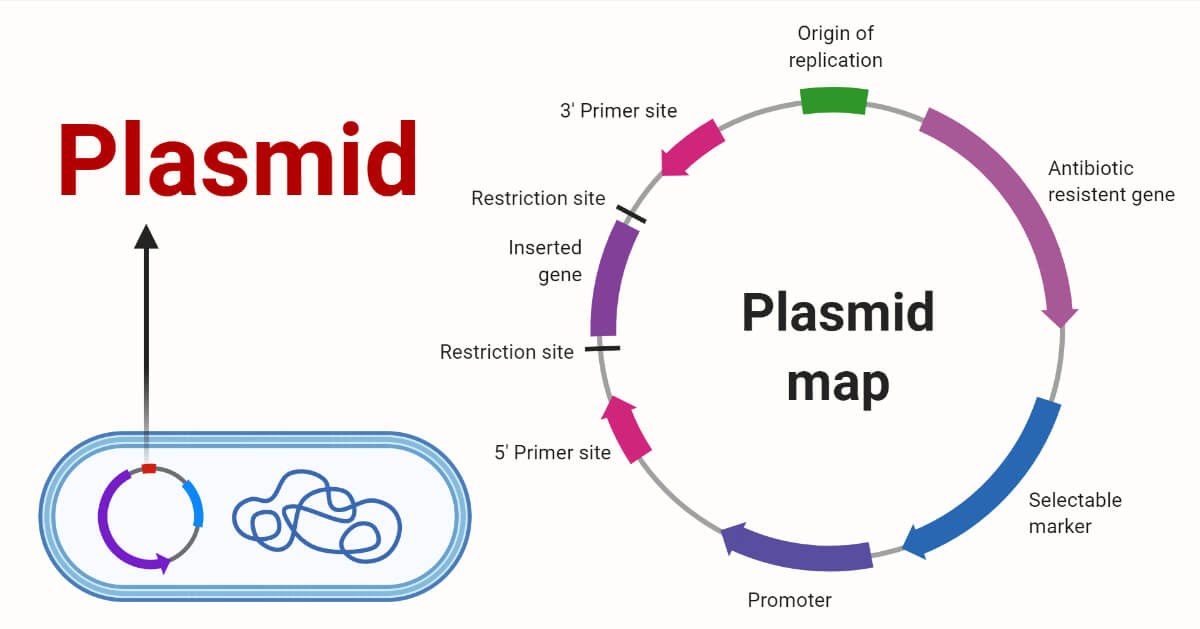
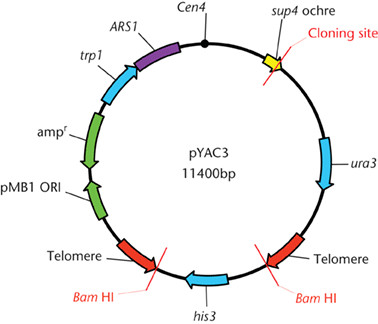
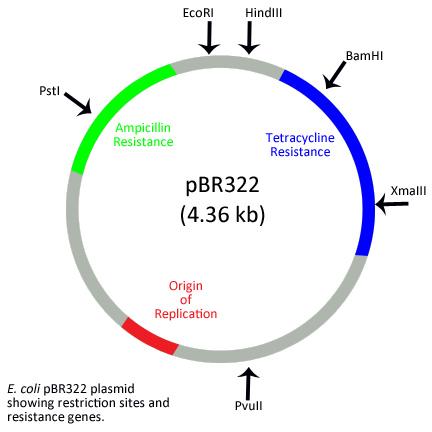
Cloning Vectors- Definition, Characteristics, Types, Uses - Microbe Notes Vectors have been developed and adapted for a wide range of uses. Two primary uses are: (1) to isolate, identify, and archive fragments of a larger genome. (2) to selectively express proteins encoded by specific genes. Vectors were the first DNA tools used in genetic engineering, and continue to be cornerstones of the technology.
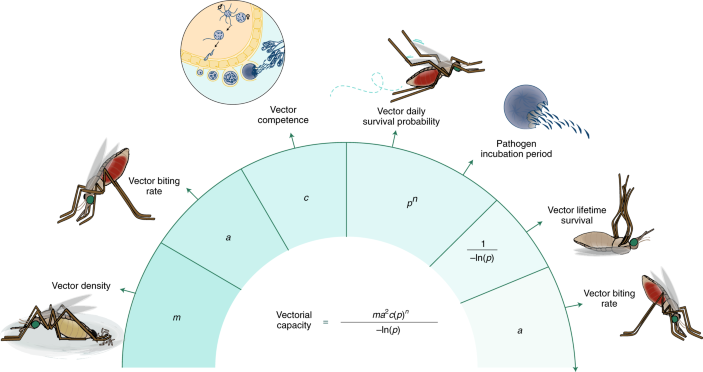
Vector Biology - National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Vectors, including insects and ticks, are capable of transmitting infectious disease pathogens among humans or between animals and humans. Diseases spread by vectors such as mosquitoes are a serious public health problem, affecting nearly half of the world's population, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Vector Biology Flashcards | Quizlet Vector A carrier (usually an arthropod) that transfers an infective agent from one host to another. Malaria Affects 41% of the world. 350-500m/year cases. Transmission Physical contact with infected individuals, liquids, food, body fluids, contaminated objects and airborne inhalation cause.... Physical contact
Vector-borne diseases - World Health Organization Vector-borne diseases account for more than 17% of all infectious diseases, causing more than 700 000 deaths annually. They can be caused by either parasites, bacteria or viruses. Malaria is a parasitic infection transmitted by Anopheline mosquitoes. It causes an estimated 219 million cases globally, and results in more than 400,000 deaths ...
What is meant by a vector in microbiology? - Answers A vector is a plasmid that inserts genes into a cell through genetic engineering. A vector is a term used to refer to an organism which itself does not cause disease but allows the transmission of ...
vector | Definition from the Biology topic | Biology from longman dictionary of contemporary english vec‧tor /ˈvektə $ -ər/ noun [ countable] technical 1 a quantity such as force that has a direction as well as size 2 an insect or animal that passes disease from one person to another syn carrier mosquitoes are feared as vectors of malaria. 3 in biology, an animal or human cell that is used to carry …
Vector- Definition, Features, Types, Examples, Applications, Limitations A vector is a substance, usually a piece of DNA that carries a sequence of DNA or other genetic material and introduces it into a new cell. Vectors act as vehicles to transfer genetic material from one cell to the other for different purposes like multiplying, expressing, or isolation.
Biological vector - definition of biological vector by The Free Dictionary vec·tor (vĕk′tər) n. 1. Mathematics a. A quantity, such as velocity, completely specified by a magnitude and a direction. b. A one-dimensional array. c. An element of a vector space. 2. An organism, such as a mosquito or tick, that carries disease-causing microorganisms from one host to another. 3.
Vector - Genome.gov Definition 00:00 … A vector, as related to molecular biology, is a DNA molecule (often plasmid or virus) that is used as a vehicle to carry a particular DNA segment into a host cell as part of a cloning or recombinant DNA technique. The vector typically assists in replicating and/or expressing the inserted DNA sequence inside the host cell.
Vector Definition in Science - ThoughtCo Vector Definition in Biology and Medicine In the biological sciences, the term vector refers to an organism that transmits a disease, parasite, or genetic information from one species to another. Examples: Mosquitoes are a vector of malaria. A virus may be used as a vector to insert genes into a bacterial cell. Cite this Article
Vector (biology) - ScienceDaily Vector (biology) Traditionally in medicine, a vector is an organism that does not cause disease itself but which spreads infection by conveying pathogens from one host to another. Note: The above...



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vector-addition-141482002-599f183d9abed50011663dec.jpg)



/vector-addition-141482002-599f183d9abed50011663dec.jpg)

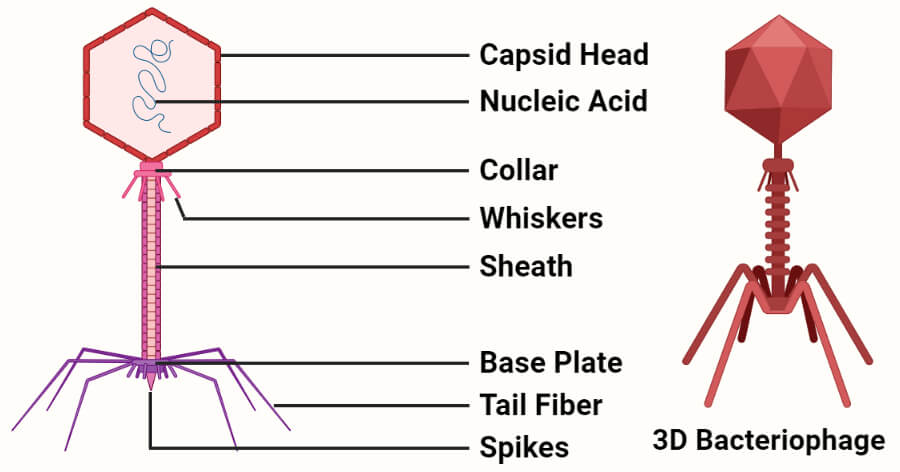



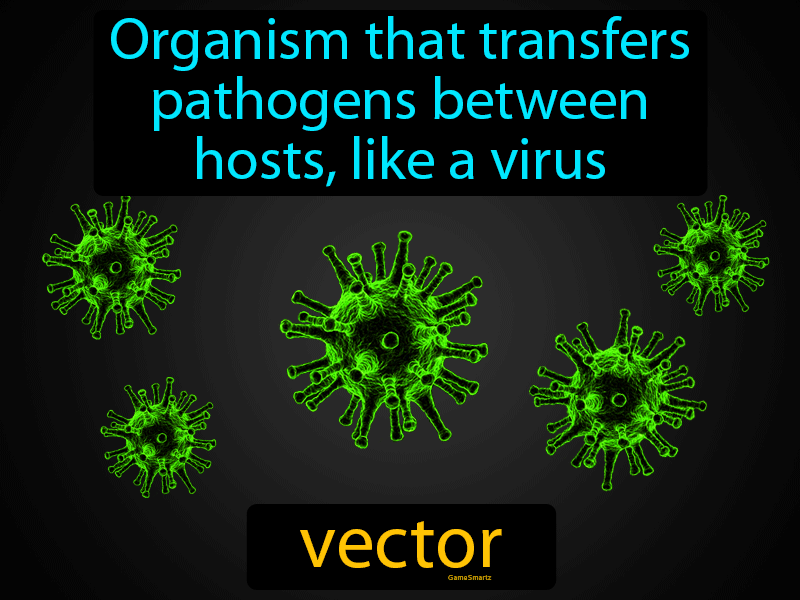

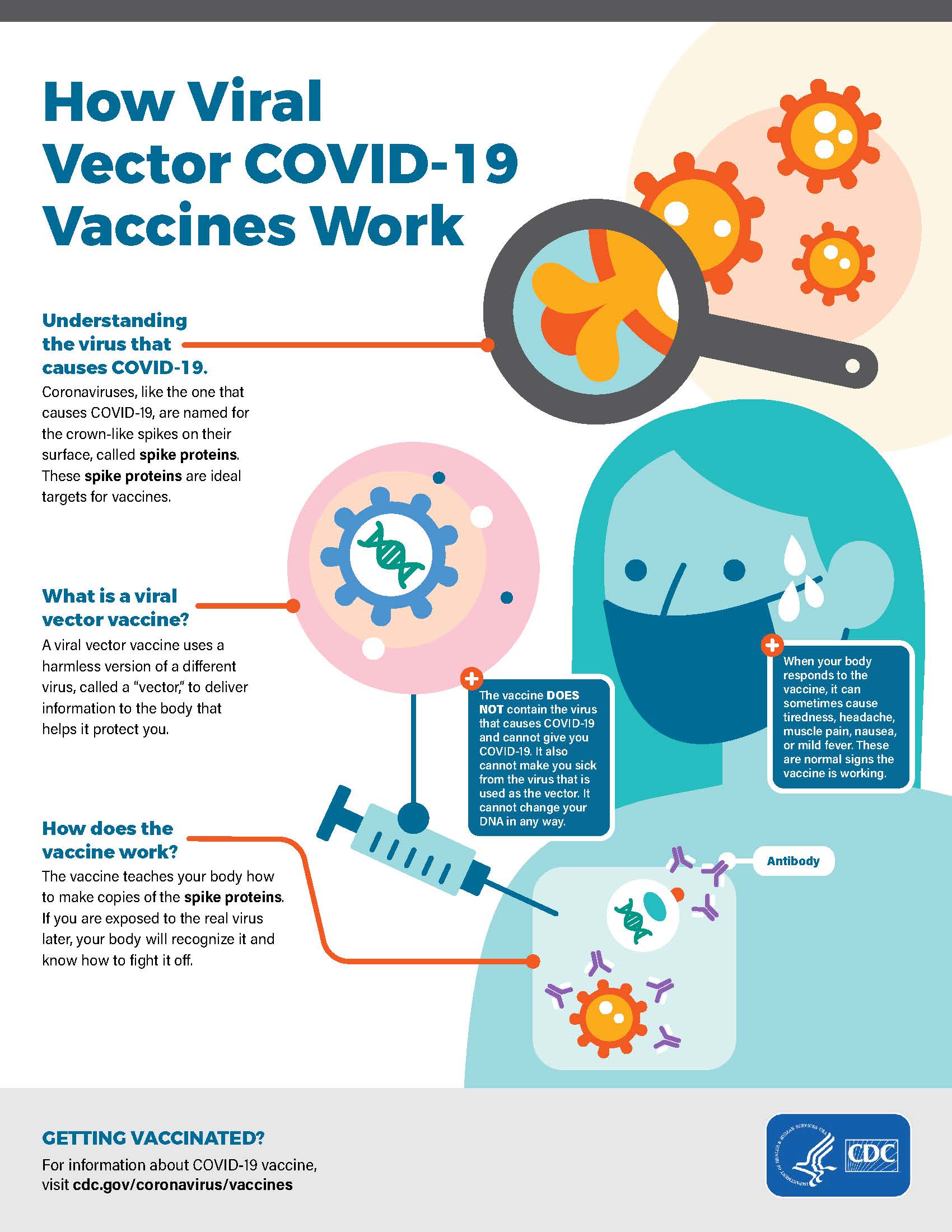







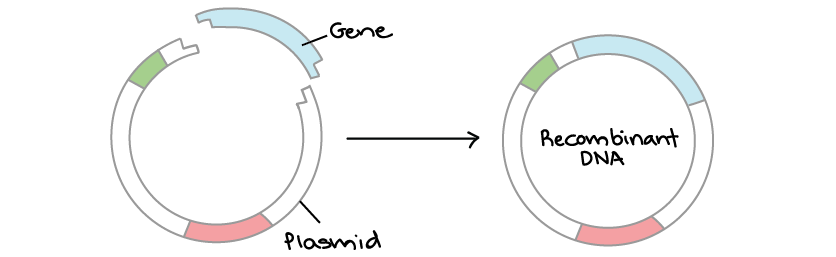
Post a Comment for "39 vector biology definition"