40 nitrogenous bases
Types of Nitrogenous Bases In RNA: Detailed Facts The nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine. RNA also has same types of nitrogenous bases yet with one only exception which is the uracil is there instead of thymine. The nitrogen have biological related material with complements of nitrogenous. Calculator for genetic nitrogenous bases guanine (G) or cytosine (C) Copy and paste the DNA sequence you want to analyze into the box. Press "Calculate" to count the bases and determine the %G~C content. Press "Clear Form" to clear all the fields, preparing the calculator for its next count. Note: If the calculator detects characters other than A, T, G, and C, it will notify you, then delete the offending ...
Calculator for genetic nitrogenous bases guanine (G) or cytosine (C) Press "Calculate" to count the bases and determine the %G~C content. Press "Clear Form" to clear all the fields, preparing the calculator for its next count. Note: If the calculator detects characters other than A, T, G, and C, it will notify you, then delete the offending characters. The calculator recognizes sequences in FASTA format, simply ...

Nitrogenous bases
Nitrogenous Bases - GSU Nitrogenous Bases. A set of five nitrogenous bases is used in the construction of nucleotides, which in turn build up the nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. These bases are crucially important because the sequencing of them in DNA and RNA is the way information is stored. The letters which form the codons in the genetic code are the A C U G of the ... Nucleosides vs Nucleotides, Purines vs Pyrimidines - Nitrogenous Bases ... This biology video tutorial provides a basic introduction into nitrogenous bases. It explains the difference Nucleosides and Nucleotides. It also discusses... Nitrogenous Bases - Definition and Structures - ThoughtCo 06.05.2019 · A nitrogenous base is an organic molecule that contains the element nitrogen and acts as a base in chemical reactions. The basic property derives from the lone electron pair on the nitrogen atom.. The nitrogen bases are also called nucleobases because they play a major role as building blocks of the nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid ().
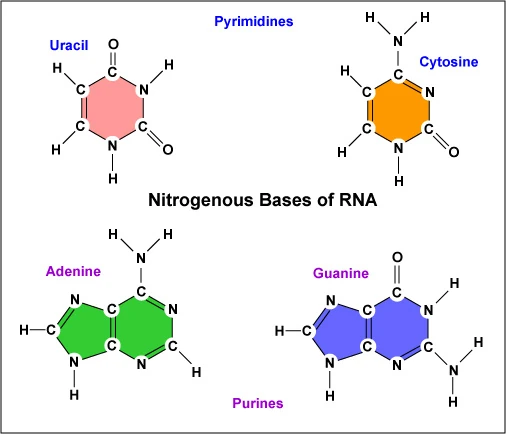
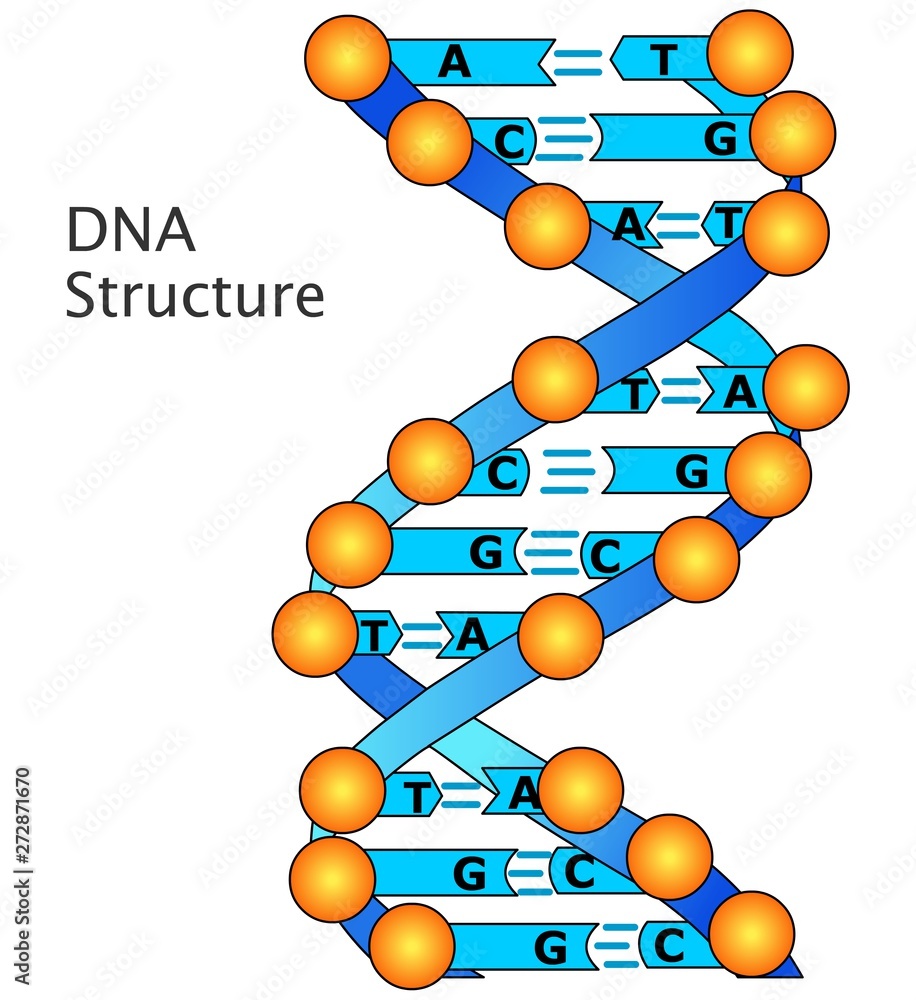
Nitrogenous bases. Nucleic Acids - Function, Examples, and Monomers - ThoughtCo 24.01.2020 · RNA has ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases A, G, C, and uracil (U). Two examples of nucleic acids include deoxyribonucleic acid (better known as DNA) and ribonucleic acid (better known as RNA). These molecules are composed of long strands of nucleotides held together by covalent bonds. Nucleobase - Wikipedia Nucleobases, also known as nitrogenous bases or often simply bases, are nitrogen -containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. Transcription and Translation | Basic Biology 31.08.2020 · There is a total of four different nitrogenous bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). A strand of DNA is almost always found bonded to another strand of DNA in a double helix. Two strands of DNA are bonded together by their nitrogenous bases. The bases form what are called ‘base pairs’ where adenine and ... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › NucleotideNucleotide - Wikipedia Apart from the five (A, G, C, T/U) bases, often degenerate bases are used especially for designing PCR primers. These nucleotide codes are listed here. Some primer sequences may also include the character "I", which codes for the non-standard nucleotide inosine. Inosine occurs in tRNAs and will pair with adenine, cytosine, or thymine.
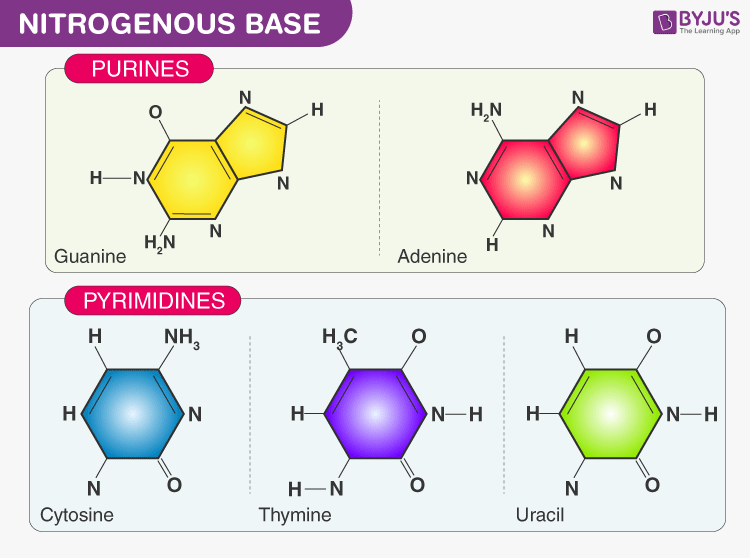
Nitrogen base Definition & Meaning | Dictionary.com or nitrogenous base noun Chemistry, Biochemistry. a nitrogen-containing organic compound that has the chemical properties of a base, especially a pyrimidine or purine: Four nitrogen bases are present in a DNA molecule. Origin of nitrogen base First recorded in 1850-55 Words nearby nitrogen base Nitrogen bases: classification and functions - science - 2022 In other words, nitrogenous bases are a part of the units that make up nucleic acids (RNA and DNA) and the other molecules mentioned. There are two main groups of nitrogenous bases: purine or purine bases and pyrimidine or pyrimidine bases. The first group includes adenine and guanine, while thymine, cytosine, and uracil are pyrimidine bases. Nitrogenous Bases in DNA & RNA | What is a Nitrogen Base Pair? Nitrogenous bases are organic molecules that contain a ring structure that includes both carbon and nitrogen atoms and can act as a base in chemical reactions. The lone pair of electrons on one of... What are the nitrogenous bases of DNA and RNA? - Quora In DNA, the four Nitrogenous bases are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine whereas in RNA they are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uridine. Some modified bases are present in tRNAs. Gaurav Kumar Singh Research scholar in biotechnology Author has 779 answers and 1.4M answer views 5 y Related Why are DNA and RNA called acids?
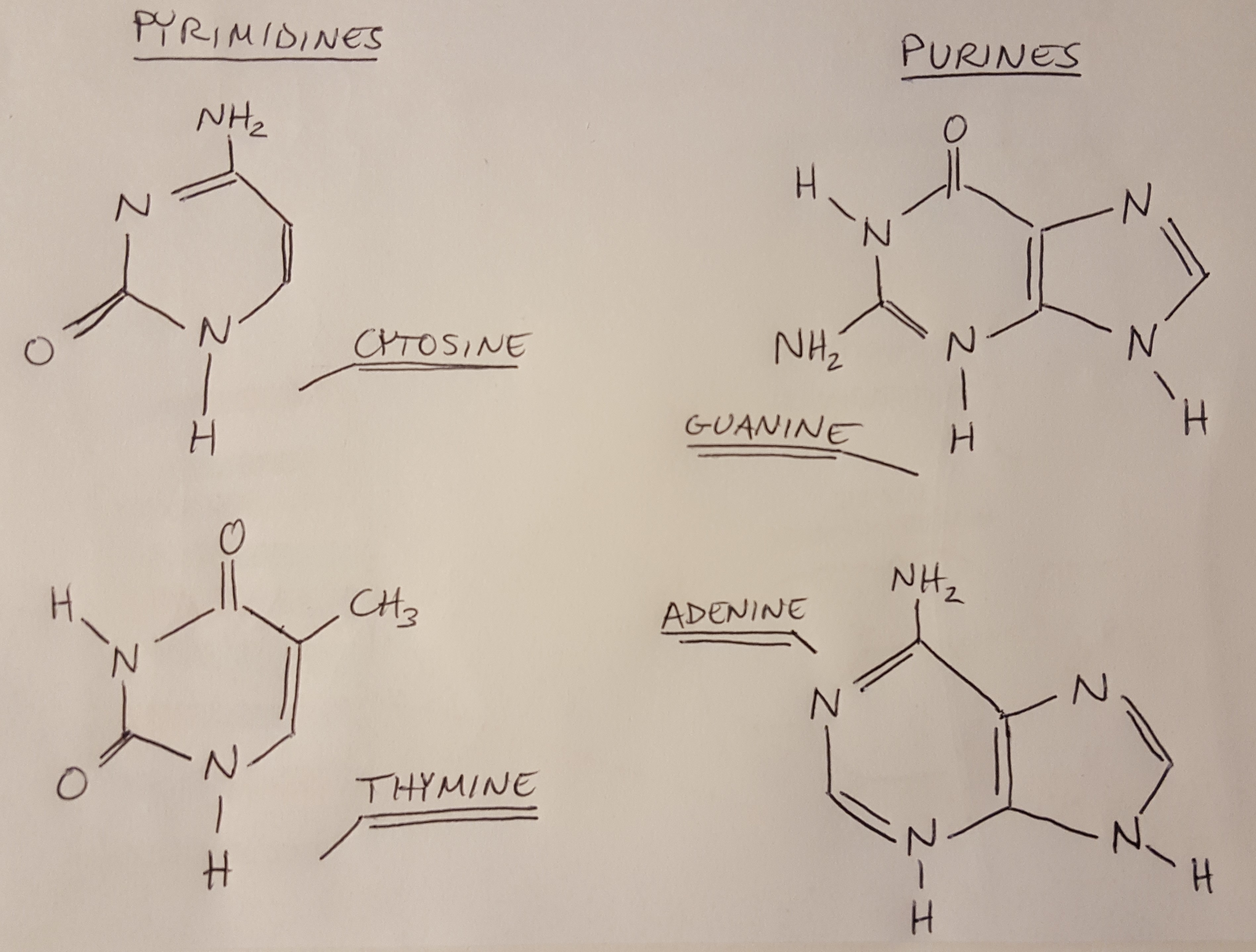
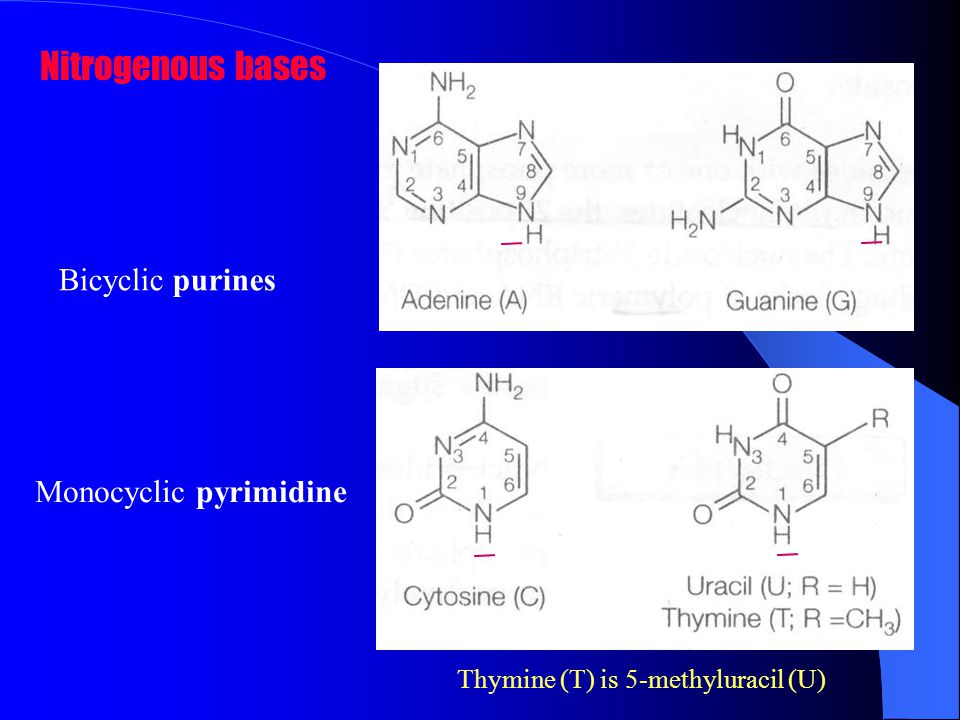
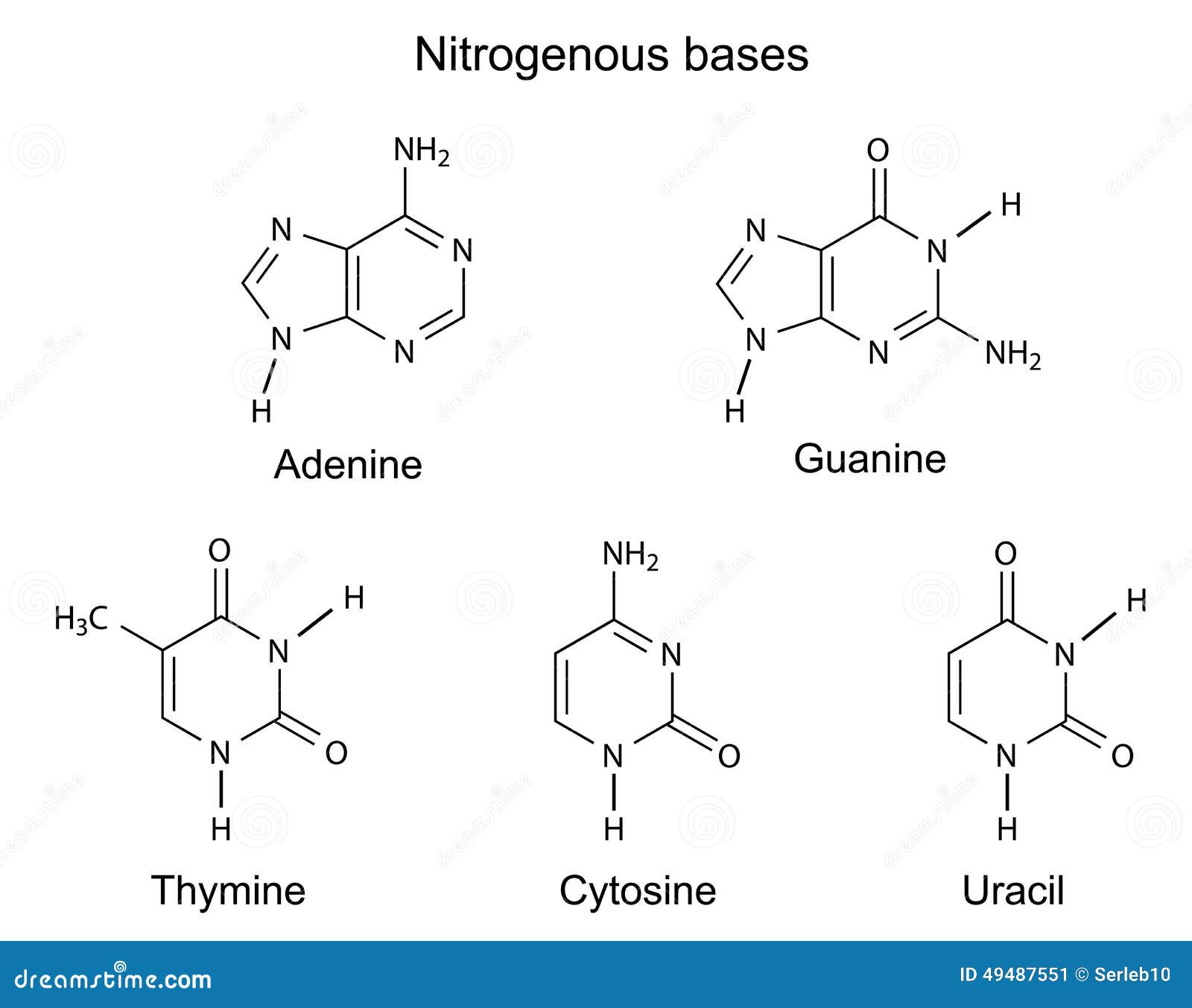
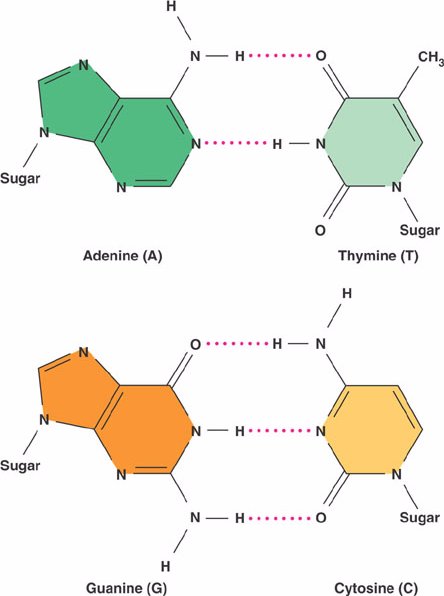
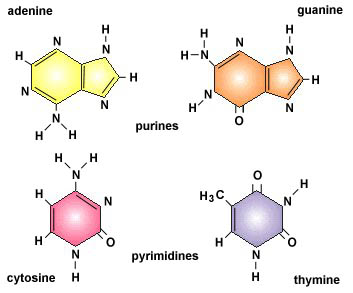
Nitrogenous Base - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Nitrogenous bases. Nucleotide hydrolysis produces two types of substances derived from the heterocyclic rings purine and pyrimidine known as the purine and pyrimidine bases. Fig. 6.1 shows their chemical structure and the numbering of the elements in the molecule. Purines are derived from pyrimidines by addition of an imidazole group. Nitrogenous Bases - Biochemistry In DNA and RNA, there are two types of nitrogenous bases: pyrimidines and purines. A pyrimidine contains one carbon-nitrogen ring with two nitrogen atoms. A purine consists of a pyrimidine fused with an imidazole ring. Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. Report an Error DNA vs. RNA | Biology Dictionary 22.01.2021 · Number of Nitrogenous Bases. DNA and RNA molecules both contain four nitrogenous bases. Three of these (adenine, cytosine, and guanine) are found in both types of nucleic acid. Sugar-Phosphate Backbone. Both DNA and RNA molecules are made up of a sugar-phosphate backbone with nucleotide bases sticking out. DNA vs. RNA structure Sequence Of Nitrogenous Bases In RNA: What, Why, Purpose, Detailed ... The five nitrogenous bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine and uracil. With the four nitrogenous bases in RNA are preferably adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil. DNA has uracil replaced by thymine. The sugar ring of five carbons and the inside of the nitrogenous bases among both the RNA and DNA are a bit different from each other.
Nitrogenous bases | definition of Nitrogenous bases by Medical dictionary base. [ bās] 1. the lowest part or foundation of anything. See also basis. 2. the main ingredient of a compound. 3. the nonacid part of a salt; a substance that combines with acids to form salts. In the chemical processes of the body, bases are essential to the maintenance of a normal acid-base balance. Excessive concentration of bases in the ...
Nitrogenous bases - SlideShare Nitrogenous bases 1. Nitrogenous Bases 2. Adenine 3. Thymine 4. Guanine 5. Cytosine 6. Nitrogenous Base Sequence G A T T A C A T G G C 7. Nitrogenous Base Sequence 1. Write the complementary base in boxes diagonally across from the given sequence. 2. Fill the top box with the complementary base from the bottom. 3.
Nitrogenous Base - Definition, Explanation, Quiz | Biology Dictionary In DNA and RNA, a nitrogenous base forms a bond with a 5-sided carbon sugar molecule, which forms a "backbone" for the entire molecule. A nitrogenous base plus this sugar backbone is known as a nucleotide, and forms the building blocks of DNA and RNA. Nitrogenous Base within Nucleic Acids Purines and Pyrimidines
biologywise.com › dna-bases-their-pairing-rulesThe 4 DNA Bases and Their Strict Pairing Rules - Biology Wise These nitrogenous bases in conjugation with a deoxyribose sugar, are called nucleosides. When they gain one or more phosphate groups, they are then termed as nucleotides. Nucleotides use these phosphate groups to link together via the formation of phosphodiester bonds, and bond to their complementary bases using hydrogen bonds.
Medical Definition of Nitrogenous base - RxList The nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), guanine ( G ), thymine (T), and cytosine (C). The nitrogenous bases in RNA are the same, with one exception: adenine (A), guanine (G), uracil (U), and cytosine (C). SLIDESHOW Healthy Resources Featured Centers Health Solutions
Nitrogenous base | definition of nitrogenous base by Medical dictionary nitrogenous base an aromatic, nitrogen-containing molecule that serves as a proton acceptor, e.g., purine or pyrimidine. ointment base a vehicle for the medicinal substances carried in an ointment. purine b's a group of compounds of which purine is the base, including uric acid, adenine, xanthine, and theobromine. Bases.
What are the 5 nitrogenous bases? - Answers The nitrogenous bases are bonded together by hydrogen bonds. What are the 5 possible nitrogenous bases? cytosine, thymine, guanine, adenine, and uracil. What are the four nitrogenous bases in mRNA?...
opentextbc.ca › biology › chapter22.4. Nitrogenous Wastes – Concepts of Biology – 1st Canadian ... Food choices that reduce the amount of nitrogenous bases in the diet help reduce the risk of gout. For example, tea, coffee, and chocolate have purine-like compounds, called xanthines, and should be avoided by people with gout and kidney stones. Figure 22.14. Gout causes the inflammation visible in this person’s left big toe joint.
What Nitrogenous Bases Are Found in DNA? - BYJUS There are four different types of nitrogenous bases present in DNA. They are adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T) and cytosine (C). Adenine and guanine are purine bases, whereas thymine and cytosine are pyrimidine bases. In a double stranded DNA, base pairing occurs between complementary bases of two strands.
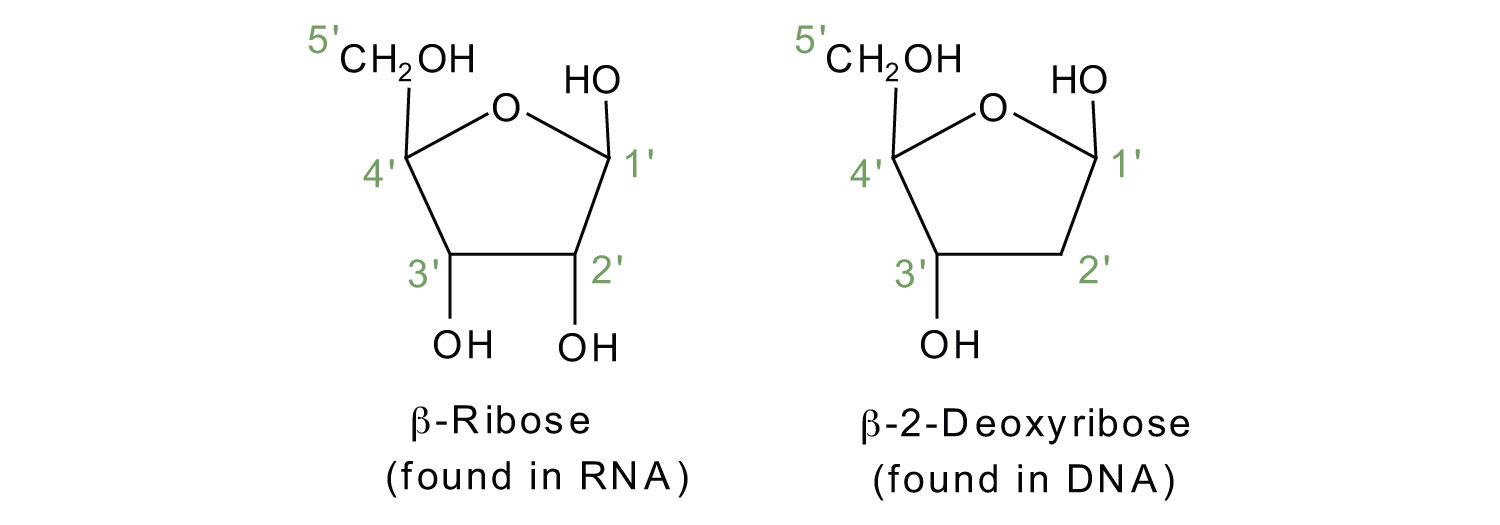
Nucleotide - Wikipedia A nucleotide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nucleobase—the two of which together are called a nucleoside—and one phosphate group.With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a "nucleoside monophosphate", "nucleoside diphosphate" or "nucleoside triphosphate", depending on how many phosphates make up the …
Nitrogenous Bases Flashcards | Quizlet nitrogenous bases that have a single ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms, such as cytosine, uracil, and thymine. Related questions. QUESTION. S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) is an organic molecule bound to various metabolic enzyme and functions transfer methyl groups from SAM to an acceptor. What is the proper designation of SAM?
Name the types of nitrogenous bases present in the DNA. 18 Answers. In DNA two types of nitrogenous base are formed :- theses are - (1) purine - is a double ring structure present in the form of adnine and guanine. (2) pyrimidine - is a single structure present in the form of cytosine and thymine. There are 4 types of nitrogenous base (i) Adenine (ii) Guanine (iii) cytosine (iv) Thymine.
Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. RNA contains uracil, instead of thymine. A nucleotide within a chain makes up the genetic material of all known living things. They also serve a number of function outside of genetic information storage, as messengers and energy moving molecules.
The 4 DNA Bases and Their Strict Pairing Rules - Biology Wise These nitrogenous bases in conjugation with a deoxyribose sugar, are called nucleosides. When they gain one or more phosphate groups, they are then termed as nucleotides. Nucleotides use these phosphate groups to link together via the formation of phosphodiester bonds, and bond to their complementary bases using hydrogen bonds. Due to the presence of deoxygenated …
nucleic acid | Definition, Function, Structure, & Types nucleic acid, naturally occurring chemical compound that is capable of being broken down to yield phosphoric acid, sugars, and a mixture of organic bases (purines and pyrimidines). Nucleic acids are the main information-carrying molecules of the cell, and, by directing the process of protein synthesis, they determine the inherited characteristics of every living thing. The two …
What Nitrogenous Bases Are Found In Rna But Not Dna - Realonomics These nitrogenous bases are Adenine (A) Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G) which are found in both RNA and DNA and then Thymine (T) which is only found in DNA and Uracil (U) which takes the place of Thymine in RNA. Nitrogenous bases can be further classified as pyrimidines or purines.Jun 1 2020.
Nitrogenous Base: The makeup of DNA and RNA - Biotech Learners Nitrogenous base, or nitrogen-containing base, is an organic molecule with a nitrogen atom that has the chemical properties of a base. The main biological function of a nitrogenous base is to bond nucleic acids together. A nitrogenous base owes its basic properties to the lone pair of electrons of a nitrogen atom.
22.4. Nitrogenous Wastes – Concepts of Biology – 1st Canadian … Gout. Mammals use uric acid crystals as an antioxidant in their cells. However, too much uric acid tends to form kidney stones and may also cause a painful condition called gout, where uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, as illustrated in Figure 22.14.Food choices that reduce the amount of nitrogenous bases in the diet help reduce the risk of gout.
› science › nucleic-acidnucleic acid | Definition, Function, Structure, & Types ... nucleic acid, naturally occurring chemical compound that is capable of being broken down to yield phosphoric acid, sugars, and a mixture of organic bases (purines and pyrimidines). Nucleic acids are the main information-carrying molecules of the cell, and, by directing the process of protein synthesis, they determine the inherited characteristics of every living thing. The two main classes of ...
Nitrogenous Bases - Definition and Structures - ThoughtCo The nitrogen bases are also called nucleobases because they play a major role as building blocks of the nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) and ribonucleic acid ( RNA ). There are two major classes of nitrogenous bases: purines and pyrimidines. Both classes resemble the molecule pyridine and are nonpolar, planar molecules.
Nucleoside vs Nucleotide - Difference and Comparison | Diffen Biological Function. Nucleotides are building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).A nucleic acid contains a chain of nucleotides linked together with covalent bonds to form a sugar-phosphate backbone with protruding nitrogenous bases. For example, DNA contains two such chains spiraling round each other in the famous double helix shape.
Nitrogenous Bases in RNA - Community College of Baltimore County Fig. 3: The Four Nitrogenous Bases in RNA: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Uracil. Adenine and guanine are also known as purine bases; cytosine and uracil are also called pyrimidine bases. Each ribonucleotide will contain one of these four bases.
DNA Structure - Visible Body A nitrogenous base is an organic molecule that contains nitrogen and has the chemical properties of a base. There are four nitrogenous bases that occur in DNA molecules: cytosine, guanine, adenine, and thymine (abbreviated as C, G, A, and T). RNA molecules contain cytosine, guanine, and adenine, but they have a different nitrogenous base ...
Nitrogenous Bases - Laboratory Notes Nitrogenous bases (also known as Nucleobases or bases) are nitrogen-containing compounds. They are an important component of nucleic acids. These bases together with ribose (sugar molecule) and phosphate form nucleotides, the monomeric unit of DNA and RNA. The following five nitrogenous bases are structural components of nucleic acids: Adenine (A)
› nucleic-acids-373552Nucleic Acids - Function, Examples, and Monomers - ThoughtCo Jan 24, 2020 · Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. DNA is composed of a phosphate-deoxyribose sugar backbone and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). RNA has ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases A, G, C, and uracil (U).
Nitrogenous Bases - Definition and Structures - ThoughtCo 06.05.2019 · A nitrogenous base is an organic molecule that contains the element nitrogen and acts as a base in chemical reactions. The basic property derives from the lone electron pair on the nitrogen atom.. The nitrogen bases are also called nucleobases because they play a major role as building blocks of the nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid ().
Nucleosides vs Nucleotides, Purines vs Pyrimidines - Nitrogenous Bases ... This biology video tutorial provides a basic introduction into nitrogenous bases. It explains the difference Nucleosides and Nucleotides. It also discusses...
Nitrogenous Bases - GSU Nitrogenous Bases. A set of five nitrogenous bases is used in the construction of nucleotides, which in turn build up the nucleic acids like DNA and RNA. These bases are crucially important because the sequencing of them in DNA and RNA is the way information is stored. The letters which form the codons in the genetic code are the A C U G of the ...




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dna-molecule-122373951-58694c055f9b586e02080af8.jpg)







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/guanine-purine-nucleobase-molecule-545861373-58692a365f9b586e02d03277.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cytosine-molecule-147216639-57afa5333df78cd39c4a5abb.jpg)












Post a Comment for "40 nitrogenous bases"